Everything You Need to Know About Rennet Enzyme and How AI Eat This Can Help
Rennet enzyme is a crucial food additive that plays a vital role in cheese production and other dairy processes. For consumers with specific dietary restrictions, religious considerations, or health concerns, identifying Rennet enzyme in food products can be challenging. The AI Eat This app revolutionizes how people manage their dietary needs by instantly scanning ingredient lists and identifying Rennet enzyme and thousands of other food additives in any language.
Understanding what Rennet enzyme is and where it appears in our food supply empowers consumers to make informed choices. Whether you're following a vegetarian diet, have religious dietary restrictions, or simply want to know what's in your food, having the right tools makes all the difference.
What Is Rennet Enzyme and Where Is It Used?
Rennet enzyme is a complex of enzymes traditionally extracted from the stomach lining of young calves, though modern food production also uses microbial and plant-based alternatives. This enzyme plays an essential role in cheese-making by coagulating milk proteins, transforming liquid milk into solid curds. The process has been used for thousands of years and remains fundamental to dairy production worldwide.
Food manufacturers use Rennet enzyme primarily in cheese production, but it also appears in various processed dairy products. The enzyme works by breaking down specific proteins in milk, creating the texture and consistency that defines different cheese varieties. Modern food technology has developed several types of rennet, including animal, vegetable, and microbial sources.
Common Foods Containing Rennet Enzyme
Rennet enzyme appears in numerous food products beyond traditional cheeses. Understanding where to look for this food additive helps consumers make better dietary choices:
- Hard and soft cheeses (cheddar, mozzarella, parmesan, brie)
- Processed cheese products and cheese spreads
- Some yogurt and kefir products
- Certain desserts and puddings containing dairy
- Processed foods with cheese ingredients
- Some protein supplements and nutritional products
Is Rennet Enzyme Safe? What Does the Research Say?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration recognizes Rennet enzyme as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) for use in food production. This designation means extensive research and historical use support its safety profile. The European Food Safety Authority has also evaluated Rennet enzyme and approved its use in food manufacturing across European Union countries.
Scientific studies consistently demonstrate that Rennet enzyme poses no significant health risks for the general population when consumed as part of normal food intake. The enzyme undergoes natural breakdown during digestion, similar to other proteins we consume daily. Regulatory agencies worldwide continue monitoring its safety through ongoing research and post-market surveillance.
Regulatory Approvals and Guidelines
International health organizations have established clear guidelines for Rennet enzyme use in food production. The World Health Organization includes rennet in its acceptable food additives list, supporting its safe use in appropriate applications. These approvals reflect decades of research and real-world usage data.
Food manufacturers must follow strict quality standards when producing and using Rennet enzyme. These regulations ensure consistent safety and efficacy across different food applications. Regular inspections and testing maintain these high standards throughout the supply chain.
Considerations for Specific Groups
While Rennet enzyme is generally safe, certain groups may need to avoid it for non-health related reasons. Vegetarians often avoid animal-derived rennet due to dietary principles, preferring plant-based or microbial alternatives. Religious dietary laws may also restrict consumption of animal-derived enzymes for some individuals.
People with severe milk allergies should exercise caution, not because of the Rennet enzyme itself, but because products containing it typically include dairy ingredients. Always consult healthcare providers about specific dietary restrictions and their implications for your health.
How AI Eat This Helps You Avoid Rennet Enzyme
The AI Eat This mobile application transforms how consumers identify Rennet enzyme in food products. Using advanced artificial intelligence and image recognition technology, the app instantly scans ingredient lists through your smartphone camera. This innovative approach eliminates guesswork and provides immediate, accurate information about food additives.
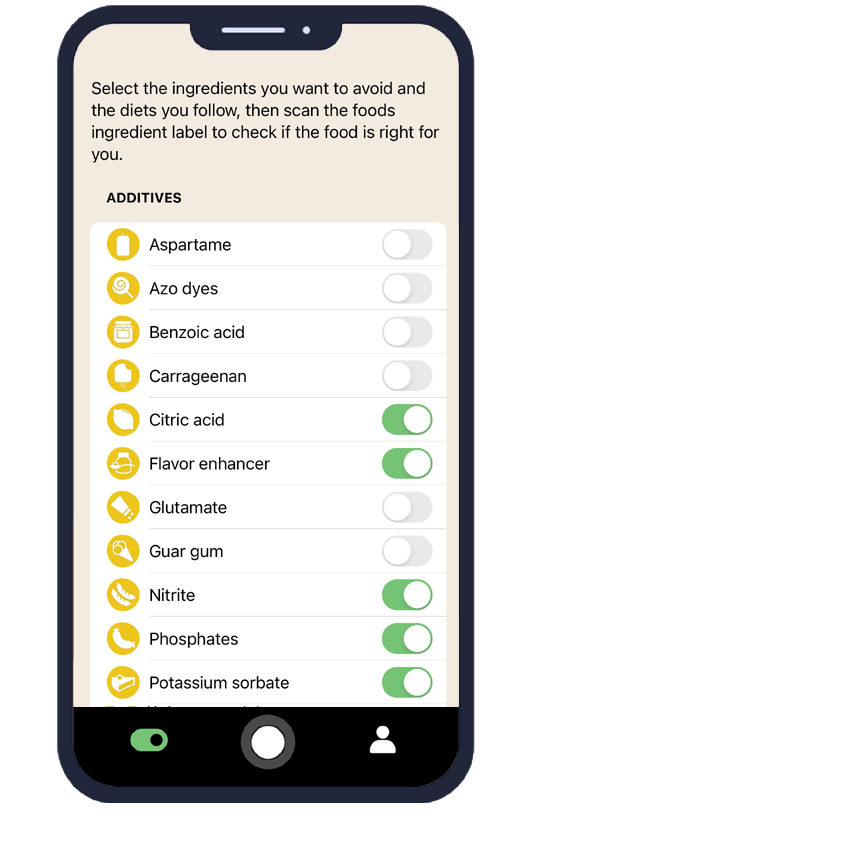
Users can set personalized dietary filters that automatically flag products containing Rennet enzyme or other unwanted ingredients. The app recognizes ingredient names in multiple languages, making it valuable for travelers or when shopping for international food products. This comprehensive approach ensures you never miss hidden sources of Rennet enzyme in your diet.
The app's database includes thousands of food additives, alternative names, and E-numbers used globally. When scanning products, AI Eat This provides detailed information about each ingredient, including Rennet enzyme safety data and dietary considerations. This educational component helps users understand their food choices better.
Who Should Consider Avoiding Rennet Enzyme?
Several groups may choose to avoid Rennet enzyme based on personal, religious, or dietary preferences. Strict vegetarians often exclude animal-derived rennet from their diets, seeking plant-based alternatives instead. Many vegetarian cheese options use microbial or vegetable rennet, providing similar functionality without animal products.
Individuals following kosher or halal dietary laws may need to verify the source and processing methods of Rennet enzyme. Religious certification organizations provide guidance on acceptable rennet sources for their communities. The AI Eat This app helps identify these ingredients quickly, supporting religious dietary observance.
Some people choose to avoid Rennet enzyme as part of broader dietary restrictions or personal food philosophies. Whether motivated by ethical concerns, environmental considerations, or simply wanting to understand food ingredients better, having reliable identification tools supports these choices.
Tips for Managing a Rennet Enzyme-Free Diet
Successfully avoiding Rennet enzyme requires strategic shopping and meal planning approaches. Reading ingredient labels carefully remains the most important step, but the AI Eat This app makes this process much more efficient and accurate. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods when possible, as these naturally contain fewer food additives.
Look for explicitly labeled vegetarian or vegan cheese products when shopping. Many manufacturers now clearly indicate when they use plant-based or microbial rennet instead of animal-derived versions. These products provide similar taste and texture while meeting specific dietary requirements.
When dining out, don't hesitate to ask restaurant staff about cheese sources and preparation methods. Many establishments can provide information about their ingredients or offer alternative options. The AI Eat This app can also help when evaluating packaged foods available in restaurants or cafeterias.
Consider exploring homemade alternatives for foods that commonly contain Rennet enzyme. Making fresh cheeses at home using plant-based rennet gives you complete control over ingredients. This approach also provides opportunities to experiment with different flavors and textures.
Conclusion
Understanding Rennet enzyme and its presence in food products empowers consumers to make informed dietary choices. While this food additive is generally safe for consumption, various personal, religious, or dietary factors may lead individuals to avoid it. The AI Eat This application provides an invaluable tool for identifying Rennet enzyme and managing dietary restrictions effectively.
Technology continues revolutionizing how we understand and interact with our food supply. Apps like AI Eat This make it easier than ever to maintain specific diets, avoid unwanted ingredients, and feel confident about food choices. Whether you're avoiding Rennet enzyme or managing other dietary restrictions, having reliable, instant information at your fingertips transforms the shopping and eating experience.
Take control of your dietary choices today. Download AI Eat This for free testing today and discover how easy it can be to identify Rennet enzyme and thousands of other food ingredients with just a simple scan!
70 filters
With over 70 filters, you can easily avoid certain ingredients and follow your dietary preference.

Paleo
Pescetarian

Ultra-processed food

Vegan